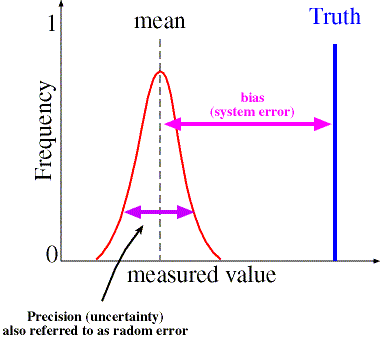
More on Bias (systematic) and Random Errors
Systematic/bias errors are consistent and repeatable (constant offset)
Random errors - arise from random fluctuations in the measurements
To differentiate between the two:
random errors are reduced when experiment is repeated many times, get a mean value - >
The systematic error (bias) will not change
systematic errors can be studied through intercomparisons, calibrations, and error propagation - very common type of error
difficulties in determining systematic errors:
"truth" is hard to know - may also have uncertainty
sub-optimal environment for comparison
random errors - studied through statistical analysis of repeated measurements (mean, standard deviation, and variance are often used)