Reactive Organic Gasses
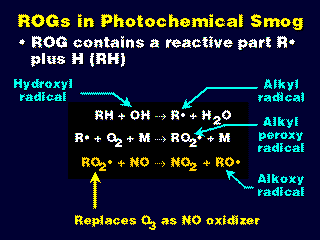
- Reactive organic gases (ROG) undergo a series of reactions to form radicals.
- The alkylperoxy radical (RO2*) reacts with and oxidizes NO to form NO2 faster than NO reacts with O3 to produce the same result.
- Thus, when ROGs are present, it is likely that O3 will not be destroyed to produce NO2, and the null cycle is broken.
- Note that each time an NO2 molecule is formed (by whatever method), it very quickly results in the production of O3 (via photo dissociation and a recombination).
recall the null
cycle: